Thursday, February 12, 2026
Transfer and Placement Committees (TPC) in the Department of Posts for recommending allotment / transfer / posting of the officials up to ASP level.
LOK SABHAUNSTARRED QUESTION
MINISTRY OF FINANCE
DEPARTMENT OF EXPENDITURE
LOK SABHA
UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.1605
TO BE ANSWERED ON MONDAY, FEBRUARY 9, 2026/MAGHA 20, 1947 (SAKA)
REVISION OF PENSION UNDER 8TH CENTRAL PAY COMMISSION
QUESTION
1605. Shri Anand Bhadauria:
Will the Minister of FINANCE be pleased to state:
(a) whether the Finance Bill, 2025 authorised the Central Government to establish distinction among pensioners on the basis of their date of retirement and a distinction may also be made among pensioners which may emanate from accepted recommendations of the Central Pay Commission;
(b) if so, whether such differentiation can also be made among pensioners on the basis of the recommendations accepted from the Central Pay Commission;
(c) if so, the details thereof and if not, the reasons therefor;
(d) whether the Central Government pensioners who have retired on or before 31st December, 2025 are likely to be covered for revision of their pension under the 8th Central Pay Commission;
(e) if so, the details thereof and if not, the reasons therefor;
(f) whether the 8th CPC has started functioning on regular basis; and
(g) if so, the details thereof and if not, the reasons for the delay?
ANSWER
MINISTER OF STATE FOR FINANCE
(SHRI PANKAJ CHOUDHARY)
(a), (b) and (c): -
The Pension of the Central Government employees is governed by the Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules, 2021 (erstwhile CCS (Pension) Rules, 1972) and the Central Civil Services (Extraordinary Pension) Rules, 2023 and instructions issued from time to time for matters connected therewith. Revision of pension is carried out through general orders issued by the Central Government, inter alia, for implementation of the accepted recommendations of the Central Pay Commission. The Central Pay Commissions being expert bodies, recommend different pay scales, allowances and pension for different categories of the Government employees. The Part-IV of Finance Act, 2025 has validated the existing Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules and principles governing pension liabilities met from the Consolidated Fund of India and does not alter or change existing Civil or Defence pensions.
(d), (e), (f) and (g):-
Government has already notified the constitution of the 8th Central Pay Commission (CPC) along-with its Terms of Reference (ToR) vide Resolution dated 03.11.2025. As per Resolution dated 03.11.2025, Commission will make its recommendations within 18 months of its constitution.
The 8th CPC has been mandated to make its recommendations on Pay, Allowances, Pension, etc. of the Central Government employees.
******************
RESS NEWS (PIB)- MINISTRY OF COMMUNICATIONS DIGITISATION OF POST OFFICE SAVINGS SCHEMES
RESS NEWS (PIB)
MINISTRY OF COMMUNICATIONS
DIGITISATION OF POST OFFICE SAVINGS SCHEMES
Posted On: 11 FEB 2026 6:27PM by PIB Delhi
Minister of State for Communications and Rural Development, Dr. Pemmasani Chandra Sekhar, in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha today, said that the Department of Posts, through a network of over 1.64 lakh post offices, serves more than 45 crore Post Office Savings Bank (POSB) account holders. To modernize and digitize Post Office Savings Schemes, Core Banking Solution (CBS) along with digital services such as ATMs, internet and mobile banking, online account opening/closure, deposits, real-time balance inquiry through online banking, fund transfers through NEFT/RTGS, IPPB–POSA linkage, etc., have been enabled in POSB through its CBS platform. In addition to facilities given to POSB customers, India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) is offering its customers a range of services such as savings and current accounts, virtual debit cards, domestic money transfer services, bill and utility payments, insurance services for IPPB customers, online payment for post office savings schemes, digital life certificates (DLC), Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS), mobile number updates in Aadhaar for any citizen, and child enrolment services for any child of 0-5 years old. All these services are contributing towards enhancing ease of access, transparency, and financial inclusion. All post offices are working on a digital platform.
The Department of Posts, through internet banking, enables transactions under the scheme such as National Savings Certificate (NSC), Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP), and Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS). These initiatives have improved customer convenience and enhanced ease of operations. MI/ARJ (Release ID: 2226580)
*********************************
संचार मंत्रालय
डाकघर बचत योजनाओं का डिजिटलीकरण
प्रविष्टि तिथि: 11 FEB 2026 6:27PM by PIB Delhi
संचार एवं ग्रामीण विकास राज्य मंत्री डॉ. पेम्मासानी चंद्र शेखर ने आज लोकसभा में एक प्रश्न के लिखित उत्तर में कहा कि डाक विभाग 164 लाख से अधिक डाकघरों के नेटवर्क के माध्यम से 45 करोड़ से अधिक डाकघर बचत बैंक (पीओएसबी) खाताधारकों को सेवाएं प्रदान करता है। डाकघर बचत योजनाओं के आधुनिकीकरण और डिजिटलीकरण के लिए, कोर बैंकिंग सॉल्यूशन (सीबीएस) के साथ-साथ एटीएम, इंटरनेट और मोबाइल बैंकिंग, ऑनलाइन खाता खोलना/बंद करना, जमा, ऑनलाइन बैंकिंग के माध्यम से वास्तविक समय में शेष राशि की जानकारी, एनईएफटी/आरटीजीएस के माध्यम से निधि हस्तांतरण, आईपीपीबी-पीओएसए लिंकेज आदि जैसी डिजिटल सेवाएं पीओएसबी के सीबीएस प्लेटफॉर्म के माध्यम से सक्षम की गई हैं। डाकघर सेवा प्रदाता (पी ओ एस बी) के ग्राहकों को दी जाने वाली सुविधाओं के अतिरिक्त, इंडिया पोस्ट पेमेंट्स बैंक (आई पी पी बी ) अपने ग्राहकों को बचत और चालू खाते, वर्चुअल डेबिट कार्ड, घरेलू धन हस्तांतरण सेवाएं, बिल और उपयोगिता भुगतान, आई पी पी बी ग्राहकों के लिए बीमा सेवाएं, डाकघर बचत योजनाओं के लिए ऑनलाइन भुगतान, डिजिटल जीवन प्रमाण पत्र (डीएलसी), आधार-सक्षम भुगतान प्रणाली (ए ई पी एस ), किसी भी नागरिक के आधार में मोबाइल नंबर अपडेट करने की सुविधा और 0-5 वर्ष की आयु के किसी भी बच्चे के लिए नामांकन सेवाएं जैसी कई सेवाएं प्रदान कर रहा है। ये सभी सेवाएं सुगम पहुंच, पारदर्शिता और वित्तीय समावेशन को बढ़ावा देने में योगदान दे रही हैं। सभी डाकघर डिजिटल प्लेटफॉर्म पर काम कर रहे हैं।
डाक विभाग इंटरनेट बैंकिंग के माध्यम से राष्ट्रीय बचत प्रमाणपत्र (एनएससी), किसान विकास पत्र (केवीपी) और वरिष्ठ नागरिक बचत योजना (एससीएसएस) जैसी योजनाओं के तहत लेनदेन को सक्षम बनाता है। इन पहलों से ग्राहकों की सुविधा में सुधार हुआ है और लेनदेन में आसानी बढ़ी है। (रिलीज़ आईडी: 2226657)
Sponsoring names for the post of Office Assistants on 'Posting in Headquarter' basis in Citizen Centric Services Directorate-reg.
DIGITISATION OF POST OFFICE SAVINGS SCHEMES
Admin Wednesday, February 11, 2026
Ministry of Communications
DIGITISATION OF POST OFFICE SAVINGS SCHEMES
Posted On: 11 FEB 2026 6:27PM by PIB Delhi
Minister of State for Communications and Rural Development, Dr. Pemmasani Chandra Sekhar, in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha today, said that the Department of Posts, through a network of over 1.64 lakh post offices, serves more than 45 crore Post Office Savings Bank (POSB) account holders. To modernize and digitize Post Office Savings Schemes, Core Banking Solution (CBS) along with digital services such as ATMs, internet and mobile banking, online account opening/closure, deposits, real-time balance inquiry through online banking, fund transfers through NEFT/RTGS, IPPB–POSA linkage, etc., have been enabled in POSB through its CBS platform. In addition to facilities given to POSB customers, India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) is offering its customers a range of services such as savings and current accounts, virtual debit cards, domestic money transfer services, bill and utility payments, insurance services for IPPB customers, online payment for post office savings schemes, digital life certificates (DLC), Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS), mobile number updates in Aadhaar for any citizen, and child enrolment services for any child of 0-5 years old. All these services are contributing towards enhancing ease of access, transparency, and financial inclusion. All post offices are working on a digital platform.
The Department of Posts, through internet banking, enables transactions under the scheme such as National Savings Certificate (NSC), Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP), and Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS). These initiatives have improved customer convenience and enhanced ease of operations.
*****
MI/ARJ
(Release ID: 2226580) Visitor Counter : 186
Read this release in: Urdu , हिन्दी , Telugu
Pay Commission8th Central Pay Commission Begins Work: Official Website Launched to Solicit Stakeholder Views and Data STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (Revised)CONTRACTUAL CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT
Revision of Pension under 8th Central Pay Commission आठवें केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग के तहत पेंशन का संशोधन: Statement submitted by Shri Pankaj Choudhary, Minister of State for Finance in Lok Sabha in reply of Unstarred Question No. 1605 asked by Shri Anand Bhadauria answered on February 9, 2026.
MINISTRY OF FINANCE
DEPARTMENT OF EXPENDITURE
LOK SABHA
UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.1605
TO BE ANSWERED ON Monday, February 9, 2026/Magha 20, 1947 (Saka)
REVISION OF PENSION UNDER 8TH CENTRAL PAY COMMISSION
QUESTION
1605. Shri Anand Bhadauria:
Will the Minister of FINANCE be pleased to state:
(a) whether the Finance Bill, 2025 authorised the Central Government to establish distinction among pensioners on the basis of their date of retirement and a distinction may also be made among pensioners which may emanate from accepted recommendations of the Central Pay Commission;
(b) if so, whether such differentiation can also be made among pensioners on the basis of the recommendations accepted from the Central Pay Commission;(c) if so, the details thereof and if not, the reasons therefor;
(d) whether the Central Government pensioners who have retired on or before 31st December, 2025 are likely to be covered for revision of their pension under the 8th Central Pay Commission;
(e) if so, the details thereof and if not, the reasons therefor;
(f) whether the 8th CPC has started functioning on regular basis; and
(g) if so, the details thereof and if not, the reasons for the delay?
ANSWER
MINISTER OF STATE FOR FINANCE
(SHRI PANKAJ CHOUDHARY)
(a), (b) and (c):The Pension of the Central Government employees is governed by the Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules, 2021 (erstwhile CCS (Pension) Rules, 1972) and the Central Civil Services (Extraordinary Pension) Rules, 2023 and instructions issued from time to time for matters connected therewith. Revision of pension is carried out through general orders issued by the Central Government, inter alia, for implementation of the accepted recommendations of the Central Pay Commission.
The Central Pay Commissions being expert bodies, recommend different pay scales, allowances and pension for different categories of the Government employees. The Part-IV of Finance Act, 2025 has validated the existing Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules and principles governing pension liabilities met from the Consolidated Fund of India and does not alter or change existing Civil or Defence pensions.
(d), (e), (f) and (g):-
Government has already notified the constitution of the 8th Central Pay Commission (CPC) along-with its Terms of Reference (ToR) vide Resolution dated 03.11.2025. As per Resolution dated 03.11.2025, Commission will make its recommendations within 18 months of its constitution.
The 8th CPC has been mandated to make its recommendations on Pay, Allowances, Pension, etc. of the Central Government employees.
भारत सरकार
वित्त मंत्रालय
व्यय विभाग
लोक सभा
लिखित प्रश्न संख्या – 1605
सोमवार 9 फरवरी; 20286/20 माघ 7947 (शक)
आठवें केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग के तहत पेंशन का संशोधन
1605. श्री आनंद भदौरिया:
क्या वित्त मंत्री यह बताने की कृपा करेंगे किः
(क) क्या वित्त विधेयक, 2025 ने केंद्र सरकार को सेवानिवृत्ति की तिथि के आधार पर पेंशनभोगियों के बीच अंतर करने के लिए अधिकृत किया है और क्या केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग की स्वीकृत सिफारिशों से उत्पन्न होने वाली आपत्तियों से पेंशनभोगियों के बीच भी अंतर किया जा सकता है;
(ख) यदि हां, तो क्या केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग द्वारा स्वीकार की गई सिफारिशों के आधार पर भी पेंशनभोगियों के बीच ऐसा अंतर किया जा सकता है;
(ग) यदि हां, तो तत्संबंधी ब्यौरा क्या है और यदि नहीं, तो इसके क्या कारण हैं;
(घ) क्या 31 दिसंबर, 2025 को या उससे पहले सेवानिवृत्त होने वाले केंद्र सरकार के पेंशनभोगियों को आववें केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग के तहत उनकी पेंशन के संशोधन के लिए कवर किए जाने की संभावना है;
(ड.) यदि हां, तो तत्संबंधी ब्यौरा क्या है और यदि नहीं, तो इसके क्या कारण हैं;
(च) क्या आठवें केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग ने नियमित आधार पर कार्य करना शुरू कर दिया है; और
(छ) यदि हां, तो तत्संबंधी ब्यौरा क्या है और यदि नहीं, तो देरी के क्या कारण हैं?
उत्तर
वित्त राज्य मंत्री
(श्री पंकज चौधरी)
(क), (ख) और (ग):-
केंद्र सरकार के कर्मचारियों की पेंशन केंद्रीय सिविल सेवा (पेंशन) नियमावली, 2021 (पूर्ववर्ती सीसीएस (पेंशन) नियमावली, 1972) और केंद्रीय सिविल सेवा (असाधारण पेंशन) नियमावली, 2023 और उससे जुड़े मामलों के लिए समय-समय पर जारी निर्देशों दवारा शासित होती है। पेंशन का संशोधन अन्य बातों के साथ-साथ केन्द्रीय वेतन आयोग की स्वीकृत सिफारिशों के कार्यान्वयन के लिए केन्द्र सरकार द्वारा जारी सामान्य आदेशों के माध्यम से किया गया है।
केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग विशेषज्ञ निकाय होने के नाते, सरकारी कर्मचारियों की विभिन्न श्रेणियाँ के लिए अलग-अलग वेतनमान, भत्ते और पेंशन की सिफारिश करता है। वित्त अधिनियम, 2029 के भाग- IV द्वारा मौजूदा केंद्रीय सिविल सेवा (पेंशन) नियमावली तथा भारत की समेकित निधि से पूरी की जाने वाली पेंशन देनदारियों को नियंत्रित करने वाले सिद्धांतों को विधिमान्य किया गया है और यह मौजूदा सिविल अथवा रक्षा पेंशन में बदलाव या परिवर्तन नहीं करता है।
(घ), (ड), (च) और (छ):-
सरकार ने 8वें केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग (सीपीसी) के गठन को अपने विचारार्थ विषयों (टीओआर) के साथ दिनांक 03.11.2025 के संकल्प के माध्यम से पहले ही अधिसूचित कर दिया है। दिनांक 03.11.2025 के संकल्प के अनुसार, आयोग इसके गठन के 18 महीने के भीतर अपनी सिफारिशें देगा।
8वें केंद्रीय वेतन आयोग को केंद्र सरकार के कर्मचारियों के वेतन, भत्ते, पेंशन इत्यादि पर अपनी सिफारिशें करने के लिए अधिदेशित किया गया है।
*****
Saturday, February 7, 2026
8th CPC started website and requested replies for qutionier from Unions, Individuals and Pensioners of Central Government
Thursday, February 5, 2026
Sponsoring names for the post of Office Assistants on 'Posting in Headquarter' basis in Citizen Centric Services Directorate-reg.
Wednesday, February 4, 2026
Clarification on 15G-15H-during claims settlement of PLI-RPLI letter dated 04.02.2026 with Annexures
Seniority List in the grade of Assistant Engineer (Civil) in the Department of Posts as on 01.01.2026
Mandatory Course Completion for Central Government Employees on the iGOT Portal and Reporting APAR for Year 2025-26 | Course Direct Link for all Officers and Officials in Department of Posts | DOP OM dated 02/02/2026
Clarification regarding the eligibility of Persons with Benchmark Disabilities possessing certificates for disabilities for the purpose of reservation in recruitment
Application for the post of Assistant Engineer (Civil) in the Ministry of Communication (Department of Posts) Civil Wing | DOP OM No.4-6/2019-CWP/10 dated 29/10/2026
Monday, February 2, 2026
Income Tax Slabs | No changes in Tax Emption in Union Budget 2026-2027
Combined Benefit of Lower Tax Slabs & Rebate
Key Highlights of the New Tax System
- If you’re self-employed or have business income, you don’t pay any tax if your income is under ₹12 lakh.
- Salaried employees pay no tax up to ₹12.75 lakh after claiming the standard deduction.
- Significant Savings for Middle-Class Families
- Households will have less tax to pay.
- More money will be left for daily needs, lifestyle expenses, and future goals.
- You can save and invest more easily.
- The tax brackets are now clearer.
- It’s easier to plan your taxes.
- The system is more transparent and straightforward.
Updates:
Follow us on WhatsApp, Telegram Channel, Twitter and Facebook for all latest updates
Introduction of ‘NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme’ as a Proof of Concept under the RSF: PFRDA Circular
Introduction of ‘NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme’ as a Proof of Concept under the Regulatory Sandbox Framework: PFRDA Circular
PENSION FUND REGULATORY AND DEVELOPMENT AUTHORITY
CIRCULAR
PFRDA/2026/07/SUP-CRA/02
Date: January 27, 2026
To
All Stakeholders under NPS
Subject: Introduction of ‘NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme’ as a Proof of Concept under the Regulatory Sandbox Framework
In furtherance of its statutory mandate under the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 2013 (‘PFRDA Act’) to protect the interests of subscribers and to promote the orderly development of the pension system, the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (‘PFRDA’ or ‘Authority’) continuously endeavours to encourage innovation within the National Pension System (‘NPS’) framework in a manner that is subscriber-centric, transparent and sustainable. With a view to examine the feasibility of integrating health-related benefit mechanisms with the existing NPS architecture and to assess the associated operational, technological and regulatory aspects, the Authority has decided to permit the introduction of NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme (‘Scheme’) as a Proof of Concept (‘PoC’) on a limited and controlled basis under the Regulatory Sandbox Framework, subject to the terms and conditions specified herein.
2. The NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme shall be introduced as a specific sector scheme under the NPS, intended exclusively to provide financial support for out-patient and in-patient medical expenses, within the framework of the Multiple Scheme Framework (‘MSF’). The Scheme shall be a contributory pension scheme, governed by the provisions of section 12(1)(a) and section 20 of the PFRDA Act and shall be offered to citizens of India on a voluntary basis.
3. The Scheme shall be launched by Pension Funds (‘PFs’), subject to prior approval of the Authority, strictly as a Proof of Concept, for a limited duration and shall operate in a controlled environment under the Regulatory Sandbox Framework. PFs may also collaborate with FinTechs and other such entities for carrying out such PoC. For the purpose of this PoC, provisions of PFRDA (Exits and Withdrawals under NPS) Regulations, 2015 have been relaxed under Regulatory Sandbox Framework.
4. The NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme shall operate in accordance with the terms specified in this Circular and Annexure–I. PFs shall ensure readiness of all systems, intermediaries and service providers, including the Central Recordkeeping Agency (‘CRA’) and Health Benefit Administrator (‘HBA’) / Third Party Administrator (TPA), prior to launch PFs shall disclose all material information relating to the Scheme, including but not limited to benefits, fees, claim processes, grievance resolution and exit provisions, in a clear and transparent manner. The PFs in consultation with the HBA may offer additional value-added features to the subscribers.
5. The Scheme shall initially be launched by PF as a Proof of Concept in collaboration with CRA and HBA/TPA, for a limited duration and with a restricted number of subscriber registrations. Upon completion of the PoC period, if the viability / feasibility of Scheme could not be established, the subscribers onboarded during PoC period shall be provided an option to transfer their accumulated corpus from the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme Account to the Common Scheme Account and thereafter exercise exit in accordance with extant PFRDA (Exits and Withdrawals under the NPS) Regulations, 2015.
6. This Circular is issued in exercise of the powers conferred upon PFRDA under the provisions of the PFRDA Act, 2013.
Yours sincerely
Digitally Sd/-
Ashish Kumar Bharati
Chief General Manager
Annexure – I
- Eligibility: Any Citizen of India is eligible for joining the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme. A Common Scheme Account shall mandatorily be opened along with the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme Account, if not already available.
- Fees and charges: Fees and charges applicable under the Scheme shall be governed by the MSF and shall be disclosed transparently. Such charges shall include charges payable to the HBA.
- Contributions: Subscribers shall be permitted to contribute any amount to the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme, in accordance with the extant guidelines applicable to the Non-Government Sector under NPS.
- Investment of contributions: Contributions under the Scheme shall be invested by the PFs in accordance with the investment guidelines prescribed under the MSF.
- Transfer of Contributions from Common Scheme Account: Subscribers (excluding subscribers under Government Sector and Government-owned Corporates), aged above 40 (forty) years shall be permitted to transfer up to 30% (thirty percent) of their self and/or employee contributions from the Common Scheme Account to the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme Account.
- Partial Withdrawals for Medical Expenses: Subscribers shall be permitted to make partial withdrawals from their NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme Account to meet outpatient or inpatient medical expenses as and when such expenses arise. At any instance, withdrawal shall be permitted up to 25% (twenty-five percent) of the subscriber’s own contributions made to the Scheme, in accordance with the provisions of the PFRDA Act, 2013. There shall be no restriction on the number of partial withdrawals and no minimum waiting period shall apply, provided that the first partial withdrawal shall be permitted only after accumulation of a minimum corpus of ₹50,000 under the Scheme.
- Premature Exit for Critical Medical Treatment: In case of inpatient medical treatment where medical expenses in a single instance exceed 70% (seventy percent) of the total corpus available in the subscriber’s NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme Account, the subscriber shall be permitted to undertake a premature exit with 100% (one hundred percent) lump sum, irrespective of the corpus size, solely for meeting such medical expenses.
- Settlement of Claims: Amounts withdrawn or exited shall be remitted directly to the concerned HBA/TPA, as applicable, based on valid claims and supporting invoices. Any surplus amount remaining after settlement of medical expenses shall be transferred to the subscriber’s Common Scheme Account.
- Exit in Other Cases: In all other cases, exit provisions applicable to All Citizens under NPS, including normal and premature exit, shall apply upon transfer of the accumulated amount from the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme Account to the Common Scheme Account.
- Grievance Redressal Mechanism: PFs, in association with the HBA/TPA, shall establish a robust grievance redressal mechanism to ensure timely and effective resolution of subscriber grievances. The responsibility for grievance resolution shall vest with the PF. CRAs shall provide necessary subscriber-level information to facilitate efficient servicing and grievance handling.
- Data Sharing and Consent: Subscriber-level data required for claim processing shall be shared with the HBA/TPA or hospital, as applicable. In compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 and rules framed thereunder, explicit digital consent shall be obtained from the subscriber by the PF or CRA at the time of activation of the NPS Swasthya Pension Scheme.
SUMMARY OF UNION BUDGET 2026-27
Ministry of Finance
SUMMARY OF UNION BUDGET 2026-27
YUVA SHAKTI-DRIVEN BUDGET EMPHASIZES ON GOVERNMENT’S ‘SANKALP’ TO FOCUS ON POOR, UNDERPRIVILEGED AND THE DISADVANTAGED
FIRST BUDGET PREPARED IN KARTAVYA BHAWAN INSPIRED BY 3 KARTAVYA
FIRST KARTAVYA IS TO ACCELERATE AND SUSTAIN ECONOMIC GROWTH
SECOND KARTAVYA IS TO FULFIL ASPIRATIONS OF PEOPLE AND BUILD THEIR CAPACITY
THIRD KARTAVYA, ALIGNED WITH VISION OF SABKA SATH, SABKA VIKAS
NEW INCOME TAX ACT, 2025 TO COME INTO EFFECT FROM APRIL 2026, SIMPLIFIED INCOME TAX RULES AND FORMS TO BE NOTIFIED SHORTLY
MULTIPLICITY OF PROCEEDINGS TO BE REDUCED TO RATIONALISE PENALTY AND PROSECUTION
DEDUCTION ALREADY AVAILABLE TO CERTAIN PRIMARY COOPERATIVE SOCIETIES TO BE EXTENDED TO CATTLE FEED AND COTTON SEED
SINGLE CATEGORY OFINFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES WITH COMMON SAFE HARBOUR MARGIN OF 15.5%
2000 CRORE THRESHOLD FOR AVAILING SAFE HARBOUR FOR IT SERVICES, UP FROM 300 CRORE RUPEES
FOREIGN CLOUD SERVICE PROVIDER TO BE GIVEN TAX HOLIDAY TILL 2047
EXEMPTION FROM MINIMUM ALTERNATE TAX TO ALL NON-RESIDENTS PAYING TAX ON PRESUMPTIVE BASIS
MINISTRY TO SET UP JOINT COMMITTEE TO MODIFY IndAS TO DO AWAY WITH SEPARATE ACCOUNTING REQUIREMENT BASED ON ICDS FROM TAX YEAR 2027-28
STT ON FUTURES TO BE RAISED TO 0.05% FROM PRESENT 0.02%
BASIC CUSTOMS DUTY EXEMPTION GIVEN TO CAPITAL GOODS USED FOR MANUFACTURING LITHIUM-ION CELLS FOR BATTERIES TO BE EXTENDED.
BASIC CUSTOMS DUTY TO THE IMPORT OF CAPITAL GOODS REQUIRED FOR PROCESSING OF CRITICAL MINERALS TO BE EXEMPTED
TARIFF RATE ON ALL DUTIABLE GOODS IMPORTED FOR PERSONAL USE TO BE REDUCED FROM 20% TO 10%
BASIC CUSTOMS DUTY ON 17 DRUGS OR MEDICINES TO BE EXEMPTED.
BIOPHARMA SHAKTI WITH AN OUTLAY OF ₹ 10,000 CRORES TO BUILD THE ECOSYSTEM FOR DOMESTIC PRODUCTION OF BIOLOGICS AND BIOSIMILARS
₹10,000 CRORE SME GROWTH FUND PROPOSED TO CREATE MSME’S AS FUTURE CHAMPIONS
PUBLIC CAPEX ENHANCED FROM ₹11.2 LAKH CRORE IN BE 2025-26 TO ₹12.2 LAKH CRORE IN FY 2026-27
SEVEN HIGH-SPEED RAIL CORRIDORS BETWEEN CITIES WILL BE DEVELOPED AS ‘GROWTH CONNECTORS’ TO PROMOTE ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE PASSENGER SYSTEMS
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF CREATIVE TECHNOLOGIES, MUMBAI TO SETUP AVGC CONTENT CREATOR LABS IN 15,000 SECONDARY SCHOOLS AND 500 COLLEGES
TO ADDRESS THE CHALLENGES FOR GIRL STUDENTS IN HIGHER EDUCATION STEM INSTITUTIONS, ONE GIRLS HOSTEL WILL BE ESTABLISHED IN EVERY DISTRICT
GOVERNMENT ANNOUNCES A SCHEME FOR UPSKILLING 10,000 GUIDES IN 20 TOURIST SITES THROUGH A STANDARDIZED, HIGH-QUALITY 12-WEEK TRAINING COURSE IN HYBRID MODE, IN COLLABORATION WITH AN IIM
KHELO INDIA MISSION TO TRANSFORM THE SPORTS SECTOR OVER THE NEXT DECADE
BHARAT-VISTAAR, A MULTILINGUAL AI TOOL TO INTEGRATE THE AGRISTACK PORTALS AND THE ICAR PACKAGE ON AGRICULTURAL PRACTICES WITH AI SYSTEMS
OVERSEAS TOUR PROGRAM PACKAGE REDUCED FROM THE CURRENT 5 PERCENT AND 20 PERCENT TO 2 PERCENT
CUSTOMS WAREHOUSING FRAMEWORK TO BE TRANSFORMED INTO A WAREHOUSE OPERATOR-CENTRIC SYSTEM WITH SELF-DECLARATIONS, ELECTRONIC TRACKING AND RISK-BASED AUDIT
CARGO CLEARANCE APPROVALS FROM VARIOUS GOVERNMENT AGENCIES TO BE SEAMLESSLY PROCESSED THROUGH A SINGLE AND INTERCONNECTED DIGITAL WINDOW BY END OF THE FINANCIAL YEAR
Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2026-2027 in Parliament today.
PART-A
On the sacred occasion of Magha Purnima and the birth anniversary of Guru Ravidas, the Finance Minister said, as this is the first Budget prepared in Kartavya Bhawan, it is inspired by 3 kartavya:
- First kartavya is to accelerate and sustain economic growth, by enhancing productivity and competitiveness, and building resilience to volatile global dynamics.
- Second kartavya is to fulfil aspirations of people and build their capacity, making them strong partners in India’s path to prosperity
- Third kartavya, aligned with vision of Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas, is to ensure that every family, community, region and sector has access to resources, amenities and opportunities for meaningful participation.
Presenting the Yuva Shakti-driven Budget which emphasizes on Government’s ‘Sankalp’ to focus on poor, underprivileged and the disadvantaged, the Finance Minister said, India will continue to take confident steps towards Viksit Bharat, balancing ambition with inclusion. As a growing economy with expanding trade and capital needs, India must also remain deeply integrated with global markets, exporting more and attracting stable long-term investment.
She also mentioned that the country is facing an external environment in which trade and multilateralism are imperilled and access to resources and supply chains are disrupted. New technologies are transforming production systems while sharply increasing demands on water, energy and critical minerals.
The Finance Minister said that after the Prime Minister’s announcement on Independence Day in 2025, over 350 reforms have been rolled out. These include GST simplification, notification of Labour Codes, and rationalisation of mandatory Quality Control Orders. High Level Committees have been formed and in parallel, the Central Government is working with the State Governments on deregulation and reducing compliance requirements.
Under the first kartavya to accelerate and sustain economic growth, interventions were proposed in six areas:
- Scaling up manufacturing in 7 strategic and frontier sectors;
- Rejuvenating legacy industrial sectors;
- Creating “Champion MSMEs”;
- Delivering a powerful push to Infrastructure;
- Ensuring long-term energy security and stability; and
- Developing City Economic Regions
To develop India as a global Biopharma manufacturing hub, the Biopharma SHAKTI with an outlay of ₹ 10,000 crores to build the ecosystem for domestic production of biologics and biosimilars will be set up over the next 5 years. The Strategy will include a Biopharma-focused network with 3 new National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER) and upgrading 7 existing ones. It will also create a network of over 1000 accredited India Clinical Trials sites. The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation will be strengthened to meet global standards and approval timeframes through a dedicated scientific review cadre and specialists.
For the labour-intensive Textile Sector, an Integrated Programme with 5 sub-parts was proposed: The National Fibre Scheme for self-reliance in natural fibres such as silk, wool and jute, man-made fibres, and new-age fibres; Textile Expansion and Employment Scheme to modernise traditional clusters with capital support for machinery, technology upgradation and common testing and certification centres; A National Handloom and Handicraft programme to integrate and strengthen existing schemes and ensure targeted support for weavers and artisans; Tex-Eco Initiative to promote globally competitive and sustainable textiles and apparels; Samarth 2.0 to modernize and upgrade the textile skilling ecosystem through collaboration with industry and academic institutions.
Recognising MSMEs as a vital engine of growth, a dedicated ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund was proposed to create future Champions, incentivizing enterprises based on select criteria.
The Finance Minister said, Public capex has increased manifold from ₹2 lakh crore in FY2014-15 to an allocation of ₹11.2 lakh crore in BE 2025-26. In FY2026-27, she proposed to increase it to ₹12.2 lakh crore to continue the momentum.
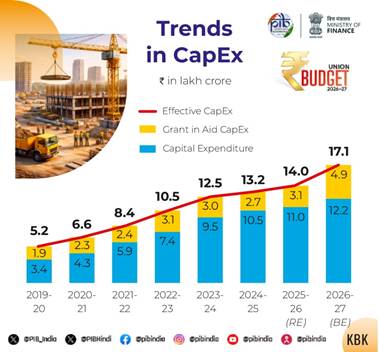
To promote environmentally sustainable movement of cargo, the Finance Minister proposed new Dedicated Freight Corridors connecting Dankuni in the East, to Surat in the West; b) operationalise 20 new National Waterways (NW) over next 5 years, starting with NW-5 in Odisha to connect mineral rich areas of Talcher and Angul and industrial centres like Kalinga Nagar to the Ports of Paradeep and Dhamra. Training Institutes will be set up as Regional Centres of Excellence for development of the required manpower.
The Budget aims to further amplify the potential of cities to deliver the economic power of agglomerations by mapping city economic regions (CER), based on their specific growth drivers. An allocation of ₹ 5000 crore per CER over 5 years is proposed for implementing their plans through a challenge mode with a reform-cum-results based financing mechanism.
To promote environmentally sustainable passenger systems, seven High-Speed Rail corridors between cities will be developed as ‘growth connectors’, namely i) Mumbai-Pune, ii) Pune-Hyderabad, iii) Hyderabad-Bengaluru, iv) Hyderabad-Chennai, v) Chennai-Bengaluru, vi) Delhi-Varanasi, vii) Varanasi-Siliguri.
The Finance Minister said that second kartavya is to fulfil aspirations and build capacity. Close to 25 crore individuals have come out of multidimensional poverty through a decade of Government’s sustained and reform-oriented efforts.
To promote India as a hub for medical tourism services, the Finance Minister proposed a Scheme to support States in establishing five Regional Medical Hubs, in partnership with the private sector. These Hubs will serve as integrated healthcare complexes that combine medical, educational and research facilities. They will have AYUSH Centres, Medical Value Tourism Facilitation Centres and infrastructure for diagnostics, post-care and rehabilitation. These Hubs will provide diverse job opportunities for health professionals including doctors and AHPs.
To scale up availability of veterinary professionals by more than 20,000, a loan-linked capital subsidy was proposed to support scheme for establishment of veterinary and para vet colleges, veterinary hospitals, diagnostic laboratories and breeding facilities in the private sector.
India’s Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming and Comics (AVGC) sector is a growing industry, projected to require 2 million professionals by 2030. The Finance Minister proposed to support the Indian Institute of Creative Technologies, Mumbai in setting up AVGC Content Creator Labs in 15,000 secondary schools and 500 colleges.
In Higher Education STEM institutions, prolonged hours of study and laboratory work pose some challenges for girl students. Through VGF/capital support, 1 girls hostel will be established in every district.
The Finance Minister proposed to set up a National Institute of Hospitality by upgrading the existing National Council for Hotel Management and Catering Technology. It will function as a bridge between academia, industry and the Government. She further proposed a pilot scheme for upskilling 10,000 guides in 20 tourist sites through a standardized, high-quality 12-week training course in hybrid mode, in collaboration with an Indian Institute of Management.
Taking forward the systematic nurturing of sports talent which is set in motion through the Khelo India programme, the Finance Minister proposed to launch a Khelo India Mission to transform the Sports sector over the next decade. The Mission will facilitate: a) An integrated talent development pathway, supported by training centres b) systematic development of coaches and support staff; c) integration of sports science and technology; d) competitions and leagues to promote sports culture and provide platforms; and, e) development of sports infrastructure for training and competition.
The Finance Minister said that the Budget’s third kartavya aligns with the vision of Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas towards a Viksit Bharat. This requires targeted efforts for increasing farmer incomes, empowering Divyangjan, empowering the vulnerable to access mental health and trauma care, focus on the Purvodaya States and the North-East Region to accelerate development and employment opportunities.
The Finance Minister proposed Bharat-VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources), a multilingual AI tool that shall integrate the AgriStack portals and the ICAR package on agricultural practices with AI systems. This will enhance farm productivity, enable better decisions for farmers and reduce risk by providing customised advisory support.
Building on the success of the Lakhpati Didi Programme, Self-Help Entrepreneur (SHE) Marts will be set up as community-owned retail outlets within the cluster level federations through enhanced and innovative financing instruments.
Reaffirming the commitment to Mental Health and Trauma Care, the Finance Minister announced to setup a NIMHANS-2 and also upgrade National Mental Health Institutes in Ranchi and Tezpur as Regional Apex Institutions.
She further proposed the development of an integrated East Coast Industrial Corridor with a well-connected node at Durgapur, creation of 5 tourism destinations in the 5 Purvodaya States, and the provision of 4,000 e-buses. She also proposed to launch a Scheme for Development of Buddhist Circuits in Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Assam, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura. The Scheme will cover preservation of temples and monasteries, pilgrimage interpretation centers, connectivity and pilgrim amenities.
Fiscal Consolidation
The debt-to-GDP ratio is estimated to be 55.6 percent of GDP in BE 2026-27, compared to 56.1 percent of GDP in RE 2025-26. A declining debt-to-GDP ratio will gradually free up resources for priority sector expenditure by reducing the outgo on interest payments. In RE 2025-26, the fiscal deficit has been estimated at par with BE of 2025-26 at 4.4 percent of GDP. In line with the new fiscal prudence path of debt consolidation, the fiscal deficit in BE 2026-27 is estimated to be 4.3 percent of GDP.
Revised Estimates 2025-26
The Revised Estimates of the non-debt receipts are ₹34 lakh crore of which the Centre’s net tax receipts are ₹26.7 lakh crore. The Revised Estimate of the total expenditure is ₹49.6 lakh crore, of which the capital expenditure is about ₹11 lakh crore.
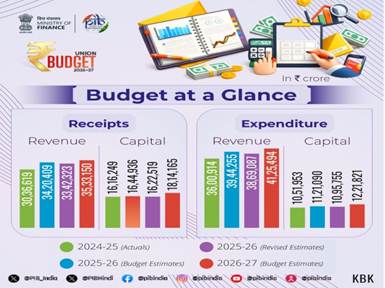
Budget Estimates 2026-27
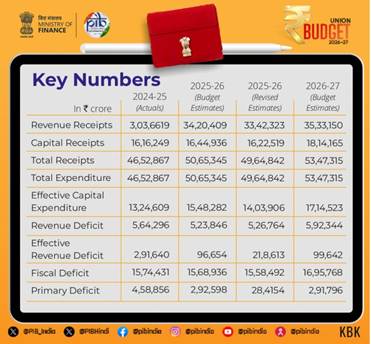
Coming
to 2026-27, the non-debt receipts and the expenditure are estimated as
₹36.5 lakh croreand ₹53.5 lakh crore respectively. The Centre’s net tax
receipts are estimated at ₹28.7 lakh crore.
To finance the fiscal deficit, the net market borrowings from dated securities are estimated at ₹11.7 lakh crore. The balance financing is expected to come from small savings and other sources. The gross market borrowings are estimated at ₹17.2 lakh crore.
PART-B
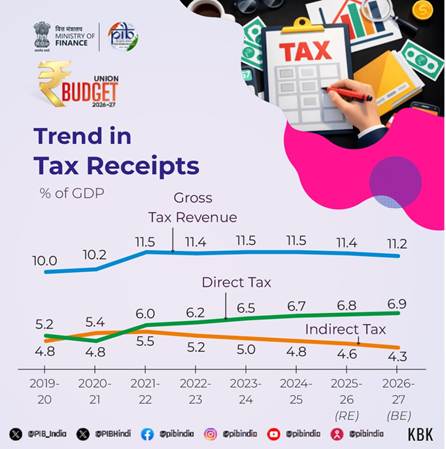
Direct Taxes:
In Direct Taxes, many new reforms are proposed in the Union Budget 2026-27. The New Income tax Act, 2025 will come into effect from April 2026. Also the simplified Income Tax Rules and Forms will be notified shortly. The forms for the purpose are redesigned for easy compliance of ordinary citizens.
There is also a proposed reduction in the TCS rates. The Overseas tour program package is reduced from the current 5 percent and 20 percent to 2 percent without any stipulation of amount. Further, TCS for pursuing education and for medical purposes under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) reduced from 5 percent to 2 percent.
It is also proposed that the supply of manpower services to be brought within the ambit of payment to contractors for the purpose of TDS. TDS on these services will be at the rate of either 1 percent or 2 percent only. For small taxpayers, a rule-based automated process will enable obtaining a lower or nil deduction certificate instead of filing an application with the assessing officer. Also, the time available for revising returns is proposed to be extended from 31st December to up to 31st March with the payment of a nominal fee. Further, the timeline for filing of tax returns is to be staggered.
To address practical issues of small taxpayers, a One-time 6-month foreign asset disclosure scheme for students, young professionals, tech employees, relocated NRIs, and such others to be introduced to disclose income or assets below a certain size.
Rationalising Penalty and Prosecution
With a view to rationalizing penalty and prosecution, the Union Budget 2026-27 proposes to reduce the multiplicity of proceedings. Assessment & penalty proceedings will be integrated by way of a common order for both. Further, the quantum of pre-payment will be reduced from 20 percent to 10 percent, calculated only on core tax demand. In order to reduce litigations, taxpayers will be allowed to update their returns even after reassessment proceedings have been initiated, at an additional 10 percent tax rate over and above the rate applicable for the relevant year.
The Budget proposes to extend the provisions for immunity from penalty and prosecution in the cases of under reporting, to misreporting as well. Taxpayer will need to pay 100 percent of the tax amount as an additional income tax over and above the tax and interest due. In addition, prosecution framework under the Income Tax Act will be rationalized. Non-production of books of account and documents, and requirement of TDS payment, where payment is made in kind, will be decriminalised. Non-disclosure of non-immovable foreign assets with aggregate value less than 20 lakh rupees will be provided with immunity from prosecution with retrospective effect from 1.10.2024.
Cooperatives
In her Budget speech in the Parliament today, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman stated that the deduction already available to a primary cooperative society engaged in supplying milk, oilseeds, fruits or vegetables raised or grown by its members, will be extended to also include supply of cattle feed and cotton seed produced by its members. Inter-cooperative society dividend income will be allowed as deduction under the new tax regime to the extent it is further distributed to its members. In addition, an exemption of three years is to be allowed to dividend income received by a notified national cooperative federation, on their investments made in companies up to 31.1.2026, for dividends further distributed to its member co-operatives.
Supporting IT sector as India’s growth engine
Underscoring the significance of the IT sector for India’s growth trajectory, the Budget proposes to club software development services, IT enabled services, knowledge process outsourcing services and contract R&D services relating to software development under a single category of Information Technology Services with a common safe harbour margin of 15.5 percent. Further, the threshold for availing safe harbour for IT services will be enhanced from 300 crore rupees to 2,000 crore rupees. Safe harbour for IT services shall be approved by an automated rule-driven process, and once applied by an IT Services company, the same safe harbour can be continued for a period of 5 years at a stretch.
Unilateral Advanced Pricing Agreement (APA) process for IT services is proposed to be fast-tracked with an endeavour to conclude it within two years, which can be extended by 6 months on taxpayer’s request. Further, the facility of modified returns available to the entity entering APA is to be extended to its associated entities.
Attracting global business and investment
While presenting the Union Budget 2026-27 in the Parliament today, the Union Finance and Corporate Affairs Minister said that any foreign company that provides cloud services to customers globally by using data centre services from India will be provided tax holiday till 2047. She added that a safe harbour of 15 percent on cost is to be provided if the company providing data centre services from India is a related entity. Moreover, a safe harbour will be provided to non-residents for component warehousing in a bonded warehouse at a profit margin of 2 percent of the invoice value. The resultant tax of about 0.7 percent will be much lower than in competing jurisdictions, the Union Minister said.
The Budget proposes to provide exemption from income tax for 5 years to any non-resident who provides capital goods, equipment or tooling, to any toll manufacturer in a bonded zone. To encourage vast pool of global talent to work in India for a longer period of time, exemption will be provided to global (non-India sourced) income of a non-resident expert, for a stay period of 5 years under notified schemes. Further, all non-residents who pay tax on presumptive basis, will be exempted from Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT).
Tax Administration
In a significant step towards strengthening tax administration, the Budget proposes the constitution of a Joint Committee of Ministry of Corporate Affairs and Central Board of Direct Taxes for incorporating the requirements of Income Computation and Disclosure Standards (ICDS) in the Indian Accounting Standards (IndAS) itself. Separate accounting requirement based on ICDS will be done away with from the tax year 2027-28. The definition of accountant for the purposes of Safe Harbour Rules will also be rationalized.
Other Tax Proposals
In the interest of minority shareholders, the Union Budget 2026-27 proposes that buyback for all types of shareholders will be taxed as Capital Gains. It requires promoters to pay an additional buyback tax, making effective tax 22 percent for corporate promoters and 30 percent for non-corporate promoters.
Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that TCS rate for sellers of specific goods namely alcoholic liquor, scrap and minerals will be rationalized to 2 percent and that on tendu leaves will be reduced from 5 percent to 2 percent. Another notable tax proposal is the move to raise STT on Futures to 0.05 percent from present 0.02 percent. STT on options premium and exercise of options will also be raised to 0.15 percent from the present rate of 0.1 percent and 0.125 percent, respectively.
To encourage companies to shift to the new regime, the Budget proposes that the set-off of brought forward MAT credit is to be allowed to companies only in the new regime. Set-off using available MAT credit will be allowed to an extent of 1/4th of the tax liability in the new regime. Proposing to make MAT the final tax, Smt. Sitharaman said that there will be no further credit accumulation from 1st April 2026. The rate of final tax will be reduced to 14 percent from the current MAT rate of 15 percent. Further, the brought forward MAT credit of taxpayers accumulated till 31st March 2026, will continue to be available to them for set-off as above.
Indirect Taxes:
The Finance Minister stated that the proposals for Customs and Central Excise aim to further simplify the tariff structure, support domestic manufacturing, promote export competitiveness, and correct inversion in duty.
Rationalisation of Custom Duties:
In Marine, Leather, and Textile products, the limit for duty-free imports of specified inputs used for processing seafood products for export, is to be increased from the current 1 per cent to 3 per cent of the FOB value. The duty-free imports of specified inputs, which is currently available for exports of leather or synthetic footwear will be allowed.
In Energy sector, the basic customs duty exemption given to capital goods used for manufacturing Lithium-Ion Cells for batteries will be extended and the basic customs duty on import of sodium antimonate for use in manufacture of solar glass will be exempted.
The Finance Minister added that the existing basic customs duty exemption on imports of goods required for Nuclear Power Projects will be extended till the year 2035 and the basic customs duty on specified parts used in the manufacture of microwave ovens will be exempted.
The basic customs duty to the import of capital goods required for processing of critical minerals will be exempted and the entire value of biogas while calculating the Central Excise duty payable on biogas blended CNG will be excluded.
In the Civil and Defence Aviation sector, the basic customs duty on components and parts required for the manufacture of civilian, training and other aircrafts will be exempted and the basic custom duty on raw materials imported for manufacture of parts of aircraft to be used in maintenance, repair, or overhaul requirements by Units in the Defence sector will be exempted.
Further, a special one-time measure, to facilitate sales by eligible manufacturing units in Special Economic Zone to the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) at concessional rates of duty is proposed.
To enhance the Ease of Living, the Finance Minister stated that the tariff rate on all dutiable goods imported for personal use will be reduced from 20 per cent to 10 per cent. The basic customs duty on 17 drugs or medicines will be exempted. 7 more rare diseases will be added for the purposes of exempting import duties on personal imports of drugs, medicines and Food for Special Medical Purposes (FSMP) used in their treatment.
Custom Processes:
The Custom processes to have minimal intervention for smoother and faster movement of goods. Further, Duty deferral period for Tier 2 and Tier 3 Authorised Economic Operators, known as AEOs, is to be enhanced from 15 days to 30 days. Same is extended to the eligible manufacturer-importers. The Validity period of advance ruling, binding on Customs, is proposed to be extended from the present 3 years to 5 years. The government agencies will be encouraged to leverage AEO accreditation for preferential treatment in clearing their cargo.
The Budget also proposes that the Customs warehousing framework is to be transformed into a warehouse operator-centric system with self-declarations, electronic tracking and risk-based audit.
Ease of Doing Business:
Multiple initiatives have been taken in the Ease of Doing Business sector. For instance, Cargo clearance approvals from various Government agencies to be seamlessly processed through a single and interconnected digital window by the end of the financial year. For goods not having any compliance requirement, clearance is to be done by Customs immediately after online registration is completed by the importer. The Customs Integrated System (CIS) is to be rolled out in 2 years as a single, integrated and scalable platform for all the customs processes. Also, the Utilization of non-intrusive scanning with advanced imaging and AI technology for risk assessment is to be expanded in a phased manner with the objective to scan every container across all the major ports.
The Union Budget 2026-27 makes the Fish catch by an Indian fishing vessel in Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) or on the High Seas free of duty. Landing of such fish on foreign port will be treated as export of goods. The budget also proposes complete removal of the current value cap of ₹10 lakh per consignment on courier exports-supports aspirations of India’s small businesses, artisans and start-ups to access global markets through e-commerce
The Provisions governing baggage clearance are also to be revised during international travel. Revised rules to enhance duty-free allowances in line with the present day travel realities. Further, Honest taxpayers, willing to settle disputes will be able close cases by paying an additional amount in lieu of penalty.
***
NB/SR/SNC/RC/AD/KM/RK
(Release ID: 2221458) Visitor Counter : 344820








_page-0001.jpg)
_page-0002.jpg)







